ラングトンのアリ
提供:kuhalaboWiki
目次 |
概要
- 平面が格子状に構成され、各マスが白または黒で塗られる。
- アリは各ステップで上下左右のいずれかのマスに移動することができる。アリは以下の規則に従って移動する。
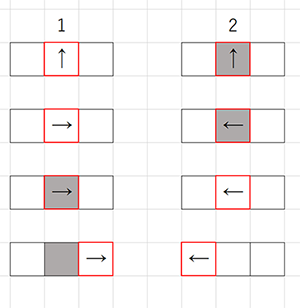
- 白いマスにアリがいた場合、90°右に方向転換し、そのマスの色を反転させ、1マス前進する。
- 黒いマスにアリがいた場合、90°左に方向転換し、そのマスの色を反転させ、1マス前進する。
この単純な規則で驚くほど複雑な動作をする。
Processingソース例
参考 ラングトンの蟻 Processing / tado Langton's ant /
- boolean型の変数の値は、true(真) か false(偽)の2値
- この場合は、cellsの色が、黒(true)か白(false)かの2値
- ! 演算子は、NOT(否定)で、!(true)はfalseのことで !(false)はtrueになる。
- 輪郭の色の指定はstroke()、塗りつぶしの色の指定は fill()
- アリの座標は、PVector型のantで表す。
- アリの進行方向は、ant_directionで表す。0(上),1(右),2(下),3(左)の4方向。
- turn rightは現在の方向に1足した値の4で割った余り。
- (ant_direction + 1) % 4; 例: 2(下)のとき、turn rightで2+1=3(左)
- turn leftは現在の方向に3足した値の4で割った余り。
- (ant_direction + 3) % 4; 例: 2(下)のとき、turn leftで(2+3)%4=1(右)
- turn rightは現在の方向に1足した値の4で割った余り。
- 初期状態 initialize_cells()
- 0 すべて 白 :しばらく彷徨った後、行進する。
- 1 すべて 黒:しばらく彷徨った後、行進する。
- 2 中央に黒い長方形 :長方形の周囲に城壁を築く。その後、行進する。
- 3 ランダム :
int CELL_NUM = 100;
int CELL_SIZE = 5;
boolean[][] cells = new boolean[CELL_NUM][CELL_NUM];
PVector ant;
int ant_direction; // 0=up, 1=right, 2=down, 3=left
void settings() {
size(CELL_NUM * CELL_SIZE, CELL_NUM * CELL_SIZE);
}
void setup(){
// initialize cells, 0: all white, 1: all black, 2: put black rectangle, 3: random
initialize_cells(0);
// initialize ant position
ant = new PVector(int(CELL_NUM / 2),int(CELL_NUM / 2));
ant_direction = 0;
}
void draw(){
// clear screen
fill(255);
rect(0, 0, width, height);
// draw cells
noStroke();
fill(30);
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
if(cells[w][h] == true){
rect(w * CELL_SIZE, h * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE);
}
}
}
// draw lines
stroke(128);
strokeWeight(1);
for(int i = 0; i < CELL_NUM; i++){
line(i * CELL_SIZE, 0, i * CELL_SIZE, height);
line(0, i * CELL_SIZE, width, i * CELL_SIZE);
}
// draw ant
fill(255, 0, 0);
rect(ant.x * CELL_SIZE, ant.y * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE);
//act ant
act_ant();
}
void act_ant(){
if(cells[(int)ant.x][(int)ant.y] == true){
ant_direction = (ant_direction + 3) % 4; // turn left
}else {
ant_direction = (ant_direction + 1) % 4; // turn right
}
cells[(int)ant.x][(int)ant.y] = !cells[(int)ant.x][(int)ant.y];
forward_ant();
}
void forward_ant(){
switch(ant_direction){
case 0:
ant.y = (ant.y - 1 + CELL_NUM) % CELL_NUM;
break;
case 1:
ant.x = (ant.x + 1) % CELL_NUM;
break;
case 2:
ant.y = (ant.y + 1) % CELL_NUM;
break;
case 3:
ant.x = (ant.x - 1 + CELL_NUM) % CELL_NUM;
break;
}
}
void initialize_cells(int method){
switch(method){
case 0: // all white
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = false;
}
}
break;
case 1: // all black
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = true;
}
}
break;
case 2: // put black rectangle
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = false;
}
}
int rect_x = 40;
int rect_y = 20;
for(int w = (CELL_NUM / 2) - int(rect_x / 2); w < (CELL_NUM / 2) + int(rect_x / 2); w++){
for(int h = (CELL_NUM / 2) - int(rect_y / 2); h < (CELL_NUM / 2) + int(rect_y / 2); h++){
cells[w][h] = true;
}
}
break;
case 3: // random
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
if(random(10) > 5){
cells[w][h] = true;
}else{
cells[w][h] = false;
}
}
}
break;
}
}
ラングトンのアリの拡張
多数の色を使うように拡張する。色の変化は、循環となり、アリの動きは各色ごとに右か左に向きを変えて1マス進むことになる。これを色の順に L(左)と R(右)を並べて表す。
- 以下のソース例
- mod = 4で、4の剰余系(0,1,2,3)で色を表す
- 色はHSB系で表す。H:色相、S:彩度、B:明度
- この例では、colorMode(HSB, mod, 100, 100)として、色相(mod=)4段階、彩度100段階、明度100段階で表す。
- 参考:色彩
- 各色(0123)による進路「LRLR」の時、彷徨った後、行進する(通常のラングトンのアリ)。
- 各色(0123)による進路「RLLR」の時、正方形を描きながら彷徨う。
- 以下のソース例は「RLLR」としている。
int CELL_NUM = 100;
int CELL_SIZE = 5;
int[][] cells = new int[CELL_NUM][CELL_NUM];
int mod = 4;
PVector ant;
int ant_direction; // 0=up, 1=right, 2=down, 3=left
void settings() {
size(CELL_NUM * CELL_SIZE, CELL_NUM * CELL_SIZE);
}
void setup(){
// initialize cells, 0: all white, 1: all black, 2: put rectangle, 3:random
colorMode(HSB, mod, 100, 100);
initialize_cells(0);
// initialize ant position
ant = new PVector(int(CELL_NUM / 2),int(CELL_NUM / 2));
ant_direction = 0;
}
void draw(){
// clear screen
fill(0,0,95);
rect(0, 0, width, height);
// draw cells
noStroke();
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
if(cells[w][h] > 0){
fill(cells[w][h], 75, 75); // セルの色
rect(w * CELL_SIZE, h * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE);
}
}
}
// draw lines
stroke(0,0,90);
strokeWeight(1);
for(int i = 0; i < CELL_NUM; i++){
line(i * CELL_SIZE, 0, i * CELL_SIZE, height);
line(0, i * CELL_SIZE, width, i * CELL_SIZE);
}
// draw ant
fill(0, 100, 100);
rect(ant.x * CELL_SIZE, ant.y * CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE);
//act ant
act_ant();
}
void act_ant(){
switch(cells[(int)ant.x][(int)ant.y]){
// RLLR
case 0:
ant_direction = (ant_direction + 1) % 4; // turn right
break;
case 1:
ant_direction = (ant_direction + 3) % 4; // turn left
break;
case 2:
ant_direction = (ant_direction + 3) % 4; // turn left
break;
case 3:
ant_direction = (ant_direction + 1) % 4; // turn right
break;
}
cells[(int)ant.x][(int)ant.y] = ( cells[(int)ant.x][(int)ant.y] + 1 ) % mod;
forward_ant();
}
void forward_ant(){
switch(ant_direction){
case 0:
ant.y = (ant.y - 1 + CELL_NUM) % CELL_NUM;
break;
case 1:
ant.x = (ant.x + 1) % CELL_NUM;
break;
case 2:
ant.y = (ant.y + 1) % CELL_NUM;
break;
case 3:
ant.x = (ant.x - 1 + CELL_NUM) % CELL_NUM;
break;
}
}
void initialize_cells(int method){
switch(method){
case 0: // all white
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = 0;
}
}
break;
case 1: // all black
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = mod/2;
}
}
break;
case 2: // put black rectangle
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = 0;
}
}
int rect_x = 40;
int rect_y = 20;
for(int w = (CELL_NUM / 2) - int(rect_x / 2); w < (CELL_NUM / 2) + int(rect_x / 2); w++){
for(int h = (CELL_NUM / 2) - int(rect_y / 2); h < (CELL_NUM / 2) + int(rect_y / 2); h++){
cells[w][h] = mod/2;
}
}
break;
case 3: // random
for(int w = 0; w < CELL_NUM; w++){
for(int h = 0; h < CELL_NUM; h++){
cells[w][h] = (int)random(mod);
}
}
break;
}
}