レイノルズのボイド
提供:kuhalaboWiki
(版間での差分)
細 (→概要) |
細 (→Processing公式サイトのソース例) |
||
| 39行: | 39行: | ||
*クラスの設計 | *クラスの設計 | ||
| − | ** Flock | + | ** Flock 鳥の群れ:Boidオブジェクトのリスト |
** Boid 1羽の鳥 | ** Boid 1羽の鳥 | ||
*** separate() 分離の加速度を計算 | *** separate() 分離の加速度を計算 | ||
2020年11月19日 (木) 00:53時点における版
目次 |
概要
ボイド(Boids)は、クレイグ・レイノルズが考案・作製した人工生命シミュレーションプログラムである。名称は「鳥もどき(bird-oid)」から取られている。コンピュータ上の鳥オブジェクトに以下の三つの動作規則を与え、多数を同時に動かして群れの振る舞いをシミュレーションする。
ボイド wiki / Reynolds Boids official /
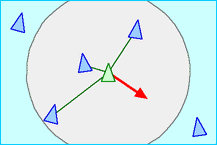
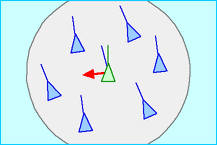
- 分離(Separation)
- 鳥は群れの鳥(Local flockmates)とぶつからないように距離をとる。
- 整列(Alignment)
- 鳥は群れの鳥(Local flockmates)と概ね同じ方向に飛ぶように速度と方向を合わせる。
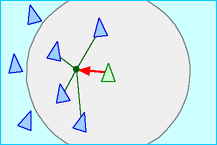
- 結合(Cohesion)
- 鳥は群れの鳥(Local flockmates)が集まっている中心方向へ向かうように方向を変える。
驚くほど自然な動きを見せ、単純な規則を用いて群としての複雑な振る舞いを再現できる。
Processing公式サイトのソース例
Birds Algorhythm Craig Reynolds Processing official より引用(一部改変)
- TWO_PI 3.1415...(円周率)×2のこと
- PVectorオブジェクトの演算
- x.normalize() ベクトルxの大きさを1にする。
- x.mag() ベクトルxの大きさを求める。
- x.add(y) 足し算 x+y
- x.sub(y) 引き算 x-y
- x.mult(y) 掛け算 x*y
- x.div(y) 割り算 x/y
- x.limit(y) 上限値 max(x,y):xの上限(最大値)はy
- dist(x,y) xとyの距離 sqrt(x*x + y*y)
- pushMatrix(), translate(x,y);rotate(theta);beginShape();vertex();endShape();popMatrix();を使った鳥(三角形)の描画
- クラスの設計
- Flock 鳥の群れ:Boidオブジェクトのリスト
- Boid 1羽の鳥
- separate() 分離の加速度を計算
- 距離がdesiredseparationの値より小さいと近すぎるとみなし、分離しようとする。
- align() 整列の加速度を計算
- 距離がneighbordistの値より小さいと近傍(群れの仲間)とみなし、整列しようとする。群れの平均速度(速さと方向)に合わせようとする。
- cohesion() 結合の加速度を計算
- 距離がneighbordistの値より小さいと近傍(群れの仲間)とみなし、結合しようとする。群れの中心に向かおうとする。
- seek(PVector target) targetを追跡(seek)する加速度の計算
- separate() 分離の加速度を計算
Flock flock;
void setup() {
size(800,800);
flock = new Flock();
// Add an initial set of boids into the system
for (int i = 0; i < 150; i++) {
flock.addBoid(new Boid(width/2,height/2));
}
}
void draw() {
background(50);
flock.run();
}
// Add a new boid into the System
void mousePressed() {
flock.addBoid(new Boid(mouseX,mouseY));
}
// The Flock (a list of Boid objects)
class Flock {
ArrayList<Boid> boids; // An ArrayList for all the boids
Flock() {
boids = new ArrayList<Boid>(); // Initialize the ArrayList
}
void run() {
for (Boid b : boids) {
b.run(boids); // Passing the entire list of boids to each boid individually
}
}
void addBoid(Boid b) {
boids.add(b);
}
}
// The Boid class
class Boid {
PVector position;
PVector velocity;
PVector acceleration;
float r; // Bird size
float maxforce; // Maximum steering force
float maxspeed; // Maximum speed
Boid(float x, float y) {
acceleration = new PVector(0, 0);
float angle = random(TWO_PI);
velocity = new PVector(cos(angle), sin(angle));
position = new PVector(x, y);
r = 2.0;
maxspeed = 2;
maxforce = 0.03;
}
void run(ArrayList<Boid> boids) {
flock(boids);
update();
borders();
render();
}
void applyForce(PVector force) {
// We could add mass here if we want A = F / M
acceleration.add(force);
}
// We accumulate a new acceleration each time based on three rules
void flock(ArrayList<Boid> boids) {
PVector sep = separate(boids); // Separation
PVector ali = align(boids); // Alignment
PVector coh = cohesion(boids); // Cohesion
// Arbitrarily weight these forces
sep.mult(1.5);
ali.mult(1.0);
coh.mult(1.0);
// Add the force vectors to acceleration
applyForce(sep);
applyForce(ali);
applyForce(coh);
}
// Method to update position
void update() {
// Update velocity
velocity.add(acceleration);
// Limit speed
velocity.limit(maxspeed);
position.add(velocity);
// Reset accelertion to 0 each cycle
acceleration.mult(0);
}
// A method that calculates and applies a steering force towards a target
// STEER = DESIRED - VELOCITY
PVector seek(PVector target) {
PVector desired = PVector.sub(target, position); // A vector pointing from the position to the target
// Scale to maximum speed
desired.normalize();
desired.mult(maxspeed);
// Steering = Desired minus Velocity
PVector steer = PVector.sub(desired, velocity);
steer.limit(maxforce); // Limit to maximum steering force
return steer;
}
void render() {
// Draw a triangle rotated in the direction of velocity
float theta = velocity.heading() + radians(90);
fill(200, 100);
stroke(255);
pushMatrix();
translate(position.x, position.y);
rotate(theta);
beginShape(TRIANGLES);
vertex(0, -r*2);
vertex(-r, r*2);
vertex(r, r*2);
endShape();
popMatrix();
}
// Wraparound
void borders() {
if (position.x < -r) position.x = width+r;
if (position.y < -r) position.y = height+r;
if (position.x > width+r) position.x = -r;
if (position.y > height+r) position.y = -r;
}
// Separation
// Method checks for nearby boids and steers away
PVector separate (ArrayList<Boid> boids) {
float desiredseparation = 25.0f; // Minimum distance
PVector steer = new PVector(0, 0);
int count = 0;
// For every boid in the system, check if it's too close
for (Boid other : boids) {
float d = PVector.dist(position, other.position);
// If the distance is greater than 0 and less than an arbitrary amount (0 when you are yourself)
if ((d > 0) && (d < desiredseparation)) {
// Calculate vector pointing away from neighbor
PVector diff = PVector.sub(position, other.position);
diff.normalize();
diff.div(d); // Weight by distance
steer.add(diff);
count++; // Keep track of how many
}
}
// Average -- divide by how many
if (count > 0) {
steer.div((float)count);
}
// As long as the vector is greater than 0
if (steer.mag() > 0) {
// Implement Reynolds: Steering = Desired - Velocity
steer.normalize();
steer.mult(maxspeed);
steer.sub(velocity);
steer.limit(maxforce);
}
return steer;
}
// Alignment
// For every nearby boid in the system, calculate the average velocity
PVector align (ArrayList<Boid> boids) {
float neighbordist = 50; // neighbor distance
PVector sum = new PVector(0, 0);
int count = 0;
for (Boid other : boids) {
float d = PVector.dist(position, other.position);
if ((d > 0) && (d < neighbordist)) {
sum.add(other.velocity);
count++;
}
}
if (count > 0) {
sum.div((float)count);
// Implement Reynolds: Steering = Desired - Velocity
sum.normalize();
sum.mult(maxspeed);
PVector steer = PVector.sub(sum, velocity);
steer.limit(maxforce);
return steer;
}
else {
return new PVector(0, 0);
}
}
// Cohesion
// For the average position (i.e. center) of all nearby boids, calculate steering vector towards that position
PVector cohesion (ArrayList<Boid> boids) {
float neighbordist = 50; // neighbor distance
PVector sum = new PVector(0, 0); // Start with empty vector to accumulate all positions
int count = 0;
for (Boid other : boids) {
float d = PVector.dist(position, other.position);
if ((d > 0) && (d < neighbordist)) {
sum.add(other.position); // Add position
count++;
}
}
if (count > 0) {
sum.div(count);
return seek(sum); // Steer towards the position
}
else {
return new PVector(0, 0);
}
}
}
クラスを使わない簡略化したソース例
クラスの設計やPVectorを使用していない例である。簡潔に記述されている。
https://garchiving.com/algorithm-of-boids-with-processing/
- 1羽の鳥の位置ベクトルは(x,y)、速度の単位ベクトルは(dx,dy)
int num = 80;
float[] x =new float[num];
float[] y =new float[num];
float[] r =new float[num];
float[] dx =new float[num];
float[] dy =new float[num];
float[] ctrDirX =new float[num];
float[] ctrDirY =new float[num];
float[] vel =new float[num];
float[] velAngle =new float[num];
float[] contX =new float[num];
float[] contY =new float[num];
float[] kX =new float[num];
float[] kY =new float[num];
float aveX, aveY, aveAngle, aveVel;
float velX, velY;
void setup() {
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
r[i] = 10;
x[i] = 250+80*cos(radians((360/num)*i));
y[i] = 250+80*sin(radians((360/num)*i));
velAngle[i] = (360/num)*i;
vel[i] = random(0, 5.5);
dx[i] = vel[i]*cos(radians(velAngle[i]));
dy[i] = vel[i]*sin(radians(velAngle[i]));
}
size(800, 800);
background(240);
smooth();
}
void draw() {
background(240);
stroke(100);
strokeWeight(1);
noFill();
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
ellipse(x[i], y[i], 10, 10);
line(x[i], y[i], x[i]+10*dx[i], y[i]+10*dy[i]);
}
// Cohesion
aveX = 0;
aveY = 0;
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
aveX += x[i];
aveY += y[i];
}
aveX /= num;
aveY /= num;
if (mousePressed == true) {
aveX = mouseX;
aveY = mouseY;
stroke(0, 0, 255);
fill(0, 0, 255);
ellipse(aveX, aveY, 10, 10);
}
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
ctrDirX[i] = aveX - x[i];
ctrDirY[i] = aveY - y[i];
}
// Align
aveVel = 0;
aveAngle = 0;
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
aveVel += sqrt(dx[i]*dx[i]+dy[i]*dy[i]);
aveAngle += degrees(atan2(dy[i], dx[i]));
}
aveVel /= num;
aveAngle /= num;
velX = aveVel*cos(radians(aveAngle));
velY = aveVel*sin(radians(aveAngle));
// Separate
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
contX[i]=0;
contY[i]=0;
for (int j=0; j<num; j++) {
if (i!=j) {
float dist=sqrt((x[j]-x[i])*(x[j]-x[i])+(y[j]-y[i])*(y[j]-y[i]));
if (0<dist&&dist<15) {
contX[i] = -1*(x[j]-x[i]);
contY[i] = -1*(y[j]-y[i]);
float temp = sqrt(contX[i]*contX[i]+contY[i]*contY[i]);
contX[i]/=temp;
contY[i]/=temp;
}
}
}
}
// Cohesion + Allgin + Separate
for (int i=0; i<num; i++) {
kX[i] = 0.03*ctrDirX[i]+4.0*velX+5.0*contX[i];
kY[i] = 0.03*ctrDirY[i]+4.0*velY+5.0*contY[i];
float tempVel = sqrt(kX[i]*kX[i]+kY[i]*kY[i]);
if (tempVel>2) {
kX[i]=2*kX[i]/tempVel;
kY[i]=2*kY[i]/tempVel;
}
dx[i] += (kX[i]-dx[i])*0.02;
dy[i] += (kY[i]-dy[i])*0.02;
x[i] += dx[i];
y[i] += dy[i];
if (x[i]>width)x[i]=0;
if (x[i]<0)x[i]=width;
if (y[i]>height)y[i]=0;
if (y[i]<0)y[i]=height;
}
}